Artificial Scarcity
Beyond the Digital
LibrePlanet 2016
Shauna Gordon-McKeon
(@shauna_gm, shaunagm@gmail.com)
Slides @ shaunagm.github.io/personal/libreplanet2016.html
Thoughts You May Have Had or Heard
Digital content like free software is easy to copy and share, so it is naturally abundant. DRM, copyright, and proprietary licensing of digital content make it artificially scarce.
Physical things do have duplication costs. They are naturally scarce (for the most part).
It is more legitimate for physical things to be scarce than for digital things to be scarce.
But...
Digital content like free software is easy to copy and share, so it is naturally abundant. DRM, copyright, and proprietary licensing of digital content make it artificially scarce.
But digital content relies on scarce resources like the creativity, expertise, enthusiasm and time of developers. There are natural and artificial scarcities in the digital world.
But...
Physical things do have duplication costs. They are naturally scarce (for the most part).
But not all physical scarcity is due to logistical constraints. Much scarcity is due to social and economic pressures. There are natural and artifical scarcities in the physical world.
But...
It is more legitimate for physical things to be scarce than for digital things to be scarce.
But there are some similarities, including space for inspiration and reason to work in solidarity.
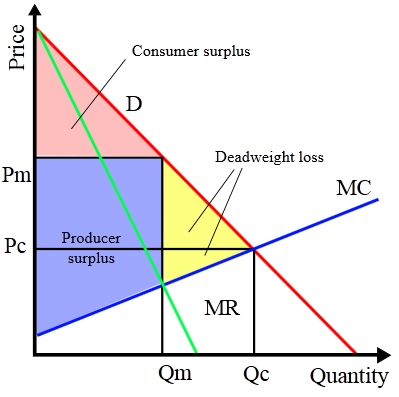
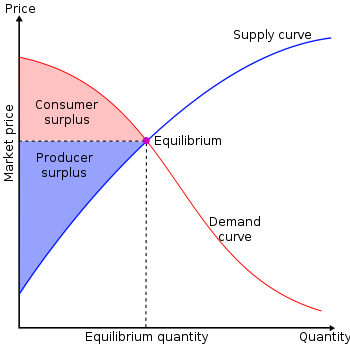
De Beers Diamond Cartel
- Lasts for over a century
- Coopt some competitors
- Threaten others by flooding sub-markets
- Started losing control in 80s and 90s to USSR
- Other market changes include conflict diamonds and synthetic diamonds
- De Beers now owns only 40% of diamond market
Ways to Address Artificial Scarcity
(so far):
- Resist monopolies and other centralized power structures
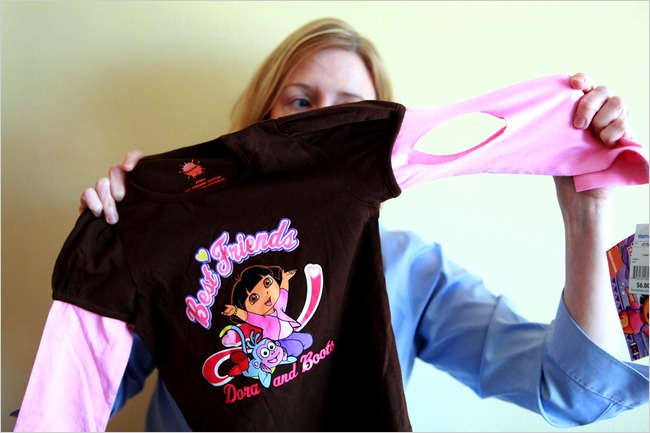

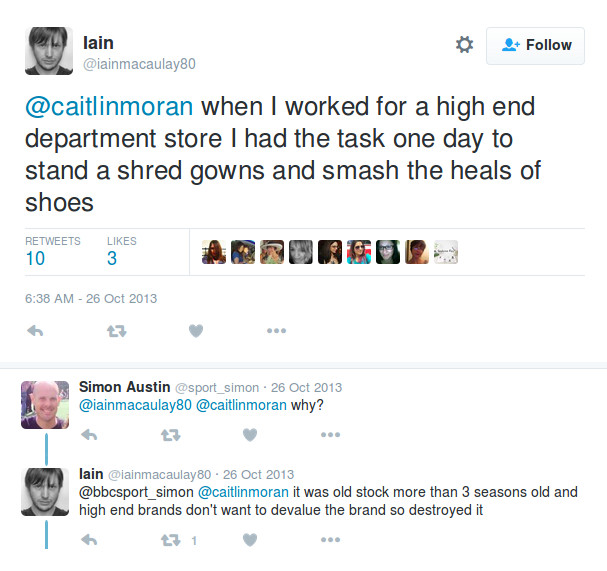
What's happening? Hard to tell...
Americans produce 25 billion pounds of textiles.
15% is recycled, about half of that to second hand clothing stores.
The other 85% goes to landfills, which makes up 5% of total landfill content.
Are donations mostly unused clothes from retailers or used clothes from consumers?
Does donating instead of recycling/dumping actually affect company profits?
"If you give away clothes,
people will stop paying for them."


Free software signals
- “Free software people are tech wizards!”
- “Free software people are political idealists.”
- “Free software people are privileged white guys.”
Outreachy.org
Ways to Address Artificial Scarcity
(so far):
- Resist monopolies and other centralized power structures
- Address supply and demand
- Signal inclusivity, not exclusivity
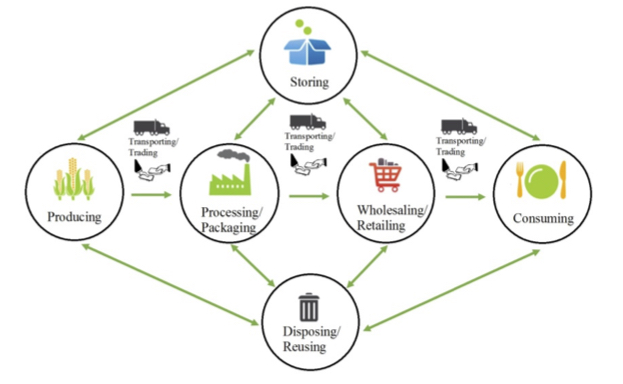
Other Issues
- Fear of liability
- All things aren't equal (or interchangeable)
- Donating takes effort!
Ways to Address Artificial Scarcity
(so far):
- Resist monopolies and other centralized power structures
- Address supply and demand
- Signal inclusivity, not exclusivity
- Address liability
- Consider government intervention
- Lower friction so software is more interchangable
- Improve cost/benefit ratio for contributing
Housing Vacancy Breakdown
(data from the US Census Bureau)
- 87.2% non-vacant units break down into 55.7% owner occupied and 31.5% renter occupied.
- 12.8% vacant units break down into 3.1% seasonally occupied, 2.4% for rent, 1.1% for sale, .8% sold or rented but not yet occuppied, and 5.4% held off-market for other reasons.
- Rental vacancy rates were highest in rural areas (9.0%) and lower in cities and suburbs (6.7%). Homeowner vacancy rates were higher in cities and rural areas (2.2%) and lower in suburbs (1.7%).
- Rental vacancy rates were highest in the South (9.2%) and Midwest (7.0%) and lower in the NE (5.5%) and West (4.9%). Homeowner vacancy rates were highest in the South 2.1%) and NE (2.0%) and lower in the Midwest (1.7%) and West (1.5%).
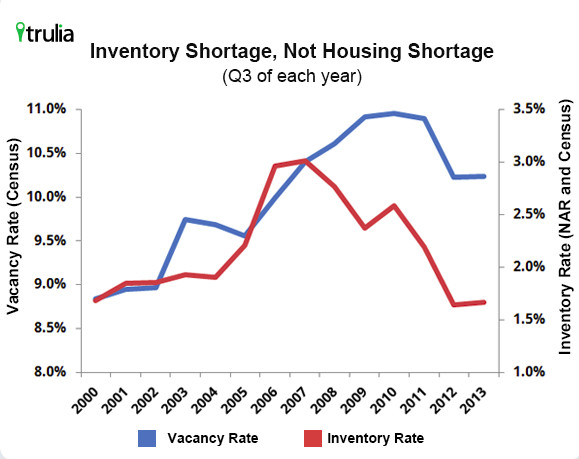
Ways to Address Artificial Scarcity
(so far):
- Resist monopolies and other centralized power structures
- Address supply and demand
- Signal inclusivity, not exclusivity
- Address liability
- Consider government intervention
- Lower friction so software is more interchangable
- Improve cost/benefit ratio for contributing
- Compassion first
Free software definition's four freedoms
- The freedom to run the program as you wish, for any purpose (freedom 0).
- The freedom to study how the program works, and change it so it does your computing as you wish (freedom 1).
- The freedom to redistribute copies so you can help your neighbor (freedom 2).
- The freedom to distribute copies of your modified versions to others (freedom 3).
What can we do?
Let's discuss!
References
Diamonds
The History of de Beers, Business Insider
Clothes
"When I worked for a high end department store..." @iainmacaulay80, Oct 26 2013
EPA report and summary
"Need a suit? These organizations will give you one – and more", Jails to Jobs
Housing
Vacancies 4th Quarter 2015, US Census Bureau
"Foreclosure Rate still "175 percent above pre-crisis norms"" - Black Knight Financial Services
"Utah is winning the war on chronic homelessness with 'Housing First' program" - LA Times
"Room for Improvement" - Mother Jones, 2015
References
Food Waste
"About 45% of all child deaths (3 million) are linked to malnutrition...." WHO, 2015
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
"80% of water goes to food production..." NPR
"If global food waste were a country..." National Geographic
"10% of the food supply is thrown out during the retail stage and 20% during the consumer stage..." USDA
"California produces..." LA Times
John Oliver's Last Week Tonight: Food Waste
Good Samaritan Food Donation Act of 1996
MA's food waste ban and follow up.
Image Credits
Herkimer Diamonds, CC0 1.0, Wikimedia Commons
Monopoly Surpluses, CC BY-SA 3.0, SilverStar on Wikimedia Commons
The Demand Curve and Consumer Surplus, Boundless.com
"Cynthia Magnus with destroyed clothing", Suzanne DeChillo/The New York Times
Get a Mac ad campaign
Tangled wires, Freegeek, Portland, Oregon, USA> by Cory Doctorow, CC BY-SA 2.0
Photo of dumped food, attribution unknown - earliest reference 2013-11-17 at meltyfood.fr
The Global Food System by FoodTechConnect
Modeling the Nation's Food System - National Science Foundation
"A worker walks past chicken eggs..." Friday, Oct. 31, 2008. AP Photo/Andy Wong
"Unemployed men queued outside a depression soup kitchen opened in Chicago by Al Capone", via U.S. National Archives and Records Administration, accessed on Wikimedia Commons
"Foreclosure", CC BY-SA 2.0 by BasicGov
"Crystal Spencer talks to her daughters in their two-bedroom apartment", Kim Raff for NationSwell
Untitled by Bill Ward, CC BY-SA 2.0
Beer Sampler by Quinn Dombrowski, CC BY-SA 2.0